
Orifice DP Flow with Gauge DDM DS-11
SKU: DDM DS-11
Manufacturer: Kirchner & Tochter
The device works according to the principle of differential pressure.
The DS11 gauge contains a rugged and uncomplicated diaphragm system. The differential pressure generates a unilateral force at the membrane which moves the diaphragm system against the measuring range springs.
download pdf datasheet
The DDM-DS11 metering orifice measures and monitors the flow rate of liquids.
The device works according to the principle of differential pressure.
At the orifice, a differential pressure drop occurs, which is square proportional to the volume flow rate passing the conduit.
The user mounts the orifice between flanges or with Rp pipe unions into the conduit. The unimpeded, straight tube length has to be 6 DN before and 4 DN behind the mounting position.
The DS11 gauge contains a rugged and uncomplicated diaphragm system. The differential pressure generates a unilateral force at the membrane which moves the diaphragm system against the measuring range springs. A centre-mounted tappet transfers motion of the diaphragm system to indicator movement and to initiating elements of the microswitches. Due to the completely mechanical functionality, no external power supply is needed. The applications of DDM-DS11 are engineering and process technology such as the monitoring of coolant streams in plants.
- with differential pressure gauge DS11
- optionally up to two microswitches
- installation between flanges as per DIN EN 1092-1, internal and external threads as per DIN EN ISO 228 or with pipe union as per ISO 7-1
- one device for all installation situations and flow directions
- suitable for liquids and gases
- no moving parts, wear-free
- calibration for standard measuring ranges or as per customer specification
- metering range 1:6
- accuracy 5% FS
Operating Principle
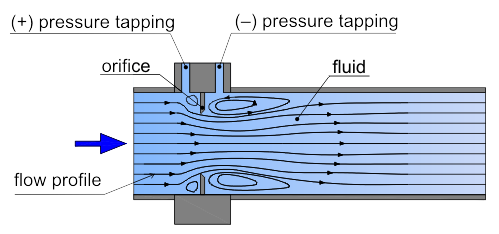
A differential pressure arises at a pipe constriction, which is proportional to the square of the flow rate through the pipe.
The resulting differential pressure can be recorded with a meter and can be directly indicated as flow rate on a scale.
